Many people experience acid reflux or heart burn from time to time, as the result of various degrees of hiatus hernia, which is partly associated with either aging or obesity. Some of them develop to actual mucosal injury at the lower esophagus, which can be diagnosed by gastroscopy. Recurrent mucosal injury at the esophagus sometimes results in mucosal degeneration called Barrett’s Esophagus, which is known to be a risk factor for Esophageal cancer.
Gastroscopy is also useful for diagnosing Helicobacter Pylori related gastritis. Since it is the definite risk factor for gastric cancer, it is important to find a various form of precancerous lesion which can frequently be found in H.Pylori related gastritis. H.Pylori related gastritis is also known to be associated with gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, and gastric mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma.
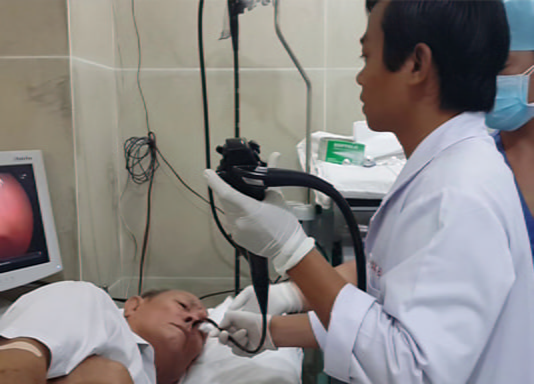
An upper endoscopy is a procedure used to visually examine the upper digestive tract using a small camera attached to the end of a long, flexible tube. In this procedure, a gastroenterologist uses an endoscopy to diagnose and sometimes treat conditions that affect the esophagus, stomach, and the beginning of the small intestine (duodenum). Upper endoscopy can be performed in an outpatient surgical center or in a hospital.
A doctor can use an endoscopy to determine the causes of digestive system signs and symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
The doctor may use endoscopy to collect tissue samples (biopsy) to look for specific diseases and conditions, such as anemia, bleeding, inflammation, diarrhea, or cancers of the digestive system.
Endoscope can also be used in treatment, as the specialist can pass special tools through an endoscope to treat problems in the digestive system, such as widening the narrow esophagus, getting rid of polyps, or removing a foreign body.
Modern endoscopes use an HD video camera to capture clearer images, as well as have a technique called narrow-band imaging (NBI), which uses a special light to help doctors better detect precancerous conditions in the digestive tract.
Although endoscopy is a very safe procedure, scientists report some rare complications. Among these complications is the risk of bleeding after the endoscopy, which increases if the operation involves removing a piece of tissue for testing (biopsy) or treating a digestive problem.
It should be noted that the risk of complications can be reduced by carefully following the instructions of the doctor who is following the case to prepare for the endoscopy, such as fasting and stopping certain medications. The patient must inform his doctor of all medications and dietary supplements that he is taking before the endoscopy. And if he is taking certain blood-thinning medications, the doctor may recommend that he stop taking them in the days leading up to the endoscopy. This is because blood-thinning medications may increase the risk of bleeding if certain procedures are performed during an endoscopy.
The endoscopy usually takes 10 to 15 minutes, depending on the patient’s condition.
When the doctor passes the endoscope down the esophagus, a small camera transmits the images to a video screen in the examination room. The doctor monitors this screen to look for problems within the upper digestive tract. If any anomalies are detected, the images are recorded for use in a subsequent examination.
Gentle air may be pumped into the esophagus to distend the digestive tract. This allows the doctor to more easily examine the folds of the digestive tract. The patient may feel pressure or full from the added air.
The doctor passes special surgical tools through the endoscope to take a tissue sample or remove any tumors and monitors the video screen to guide the tools.
The timing of the results also depends on the case. For example, if a doctor performs an endoscopy to discover an ulcer, the result may be recognized soon after the procedure. If the doctor takes a tissue sample (biopsy), the patient may have to wait several days to get results from the testing laboratory.
The recommendation of endoscopy for medical checkup is also noted. At present, the optimal screening strategy is reported to be every three years. Stomach cancer is likely to develop in a state before detection, with the intervals between examination, which are longer than three years, but screening less frequently than every three years does not seem to be more beneficial.
In the countries where gastric cancer is still prevalent such as Asia, South America, and Middle East as well, Helicobacter Pylori related gastritis is the most important and definite risk factor that is associated with the development of gastric cancer. Therefore, a patient who has a history of H.Pylori infection or has been diagnosed of H.Pylori related gastritis is recommended to be followed up by gastroscopy every 1 to 2 years depending on the state of gastritis, even after H.Pylori is successfully eradicated. In patients who have been diagnosed of no history of H.Pylori infection, a recommended interval of gastroscopy checkup can be extended to every 5 years.
胃内視鏡検査
胃内視鏡検査は、胃食道逆流症(GERD)を診断するための有用な検査です。多くの人々は、老化または肥満と関係がある軽度から重度の食道裂孔ヘルニアの結果として、時々酸逆流または胸焼けを経験します。それらのいくつかは、胃内視鏡検査によって診断することができる下部食道の肉眼的な粘膜障害に発展します。食道での反復性粘膜障害は、食道癌の危険因子であることが知られているバレット食道と呼ばれる粘膜変性を引き起こすことがあります。
胃内視鏡検査は、ヘリコバクターピロリ関連の胃炎の診断にも役立ちます。これは胃癌の明確な危険因子であるため、H.Pylori関連胃炎によく見られるさまざまな形態の前癌病変を見つけることが重要です。 H.Pyloriは、胃潰瘍、十二指腸潰瘍、および胃粘膜関連リンパ組織(MALT)リンパ腫に関連することも知られています。
上部内視鏡検査は、長くて柔軟なチューブの端に取り付けられた小さなカメラを使用して上部消化管を視覚的に検査するために使用される検査法です。この検査では、消化器医が内視鏡検査を使用して、食道、胃、および小腸(十二指腸)起始部に影響を与える状態を診断し、場合によっては治療します。上部内視鏡検査は、外来のセンターまたは病院で行うことができます。
医師は内視鏡検査を使用して、吐き気、嘔吐、腹痛、嚥下困難、胃腸出血などの消化器系の兆候や症状の原因を特定できます。
医師は内視鏡検査を使用して組織サンプルを収集し(生検)、貧血、出血、炎症、下痢、消化器系の癌などの特定の疾患や状態を診断することがあります。
内視鏡は治療にも使用できます。専門家が内視鏡に特殊な器具を通過させて、狭い食道の拡大、ポリープの除去、異物の除去などの消化器系の問題を治療できるためです。
最新の内視鏡は、HDビデオカメラを使用してより鮮明な画像をキャプチャし、狭帯域光観察(NBI)と呼ばれる技術を備えています。これは、医師が消化管の前癌状態をより適切に検出するのに役立つ特殊な光を使用します。
内視鏡検査は非常に安全な手順ですが、いくつかのまれな合併症が報告されています。 これらの合併症の中には、内視鏡検査後の出血のリスクがあります。これは、手術が検査(生検)または消化器系の問題の治療のために組織片を取り除くことを伴う場合に増加します。
合併症のリスクは、特定の薬剤の絶食や中止など、医師の指示に注意深く従うことによって減らすことができることがあります。 患者は、内視鏡検査の前に服用しているすべての薬と栄養補助食品を医師に通知する必要があります。 また、特定の抗凝血薬を服用している場合、医師は内視鏡検査に至るまでの数日間は服用を中止することを勧める場合があります。 これは、内視鏡検査中に特定の手順を実行すると、抗凝血薬が出血のリスクを高める可能性があるためです。
内視鏡検査は、患者の状態にもよりますが、通常10〜15分かかります。
医師が内視鏡を食道に通すと、小さなカメラが画像を診察室のビデオ画面に送信します。医師はこの画面を監視して、上部消化管内の問題を探します。異常が検出された場合、医師は画像を記録します。
穏やかな空気を食道に送り込み、消化管を膨張させます。これにより、医師は消化管のひだをより簡単に調べることができます。患者は、追加された空気によって圧力または満腹感を感じることがあります。
医師は、特殊な手術器具を内視鏡に通して組織サンプルを採取するか、腫瘍を取り除き、ビデオ画面を監視して器具をガイドします。
結果の時期はケースによって異なります。たとえば、医師が内視鏡検査を行って潰瘍を発見した場合、その結果は検査後すぐにわかる可能性があります。医師が組織サンプルを採取する場合(生検)、患者は検査から結果を得るまでに数日待たなければならない場合があります。
健康診断のための内視鏡検査の推奨も報告されています。現在、最適なスクリーニング戦略は3年ごとであると報告されています。胃がんは、検査の間隔が3年を超えるとその間に発症する可能性がありますが、3年ごとよりも頻度が低いスクリーニングはそれほど有益ではないようです。
アジア、南アメリカ、中東など、胃がんが依然として蔓延している国では、ヘリコバクターピロリ関連の胃炎が、胃がんの発症に関連する最も重要で明確な危険因子です。したがって、H.Pylori感染の病歴があるか、H.Pylori関連胃炎と診断された患者は、H.Pyloriの除菌が成功した後でも、胃炎の状態に応じて1〜2年ごとに胃内視鏡検査を行うことが勧められます。H.Pylori感染の病歴がないと診断された患者では、胃内視鏡検査の推奨間隔を5年ごとに延長することができます。