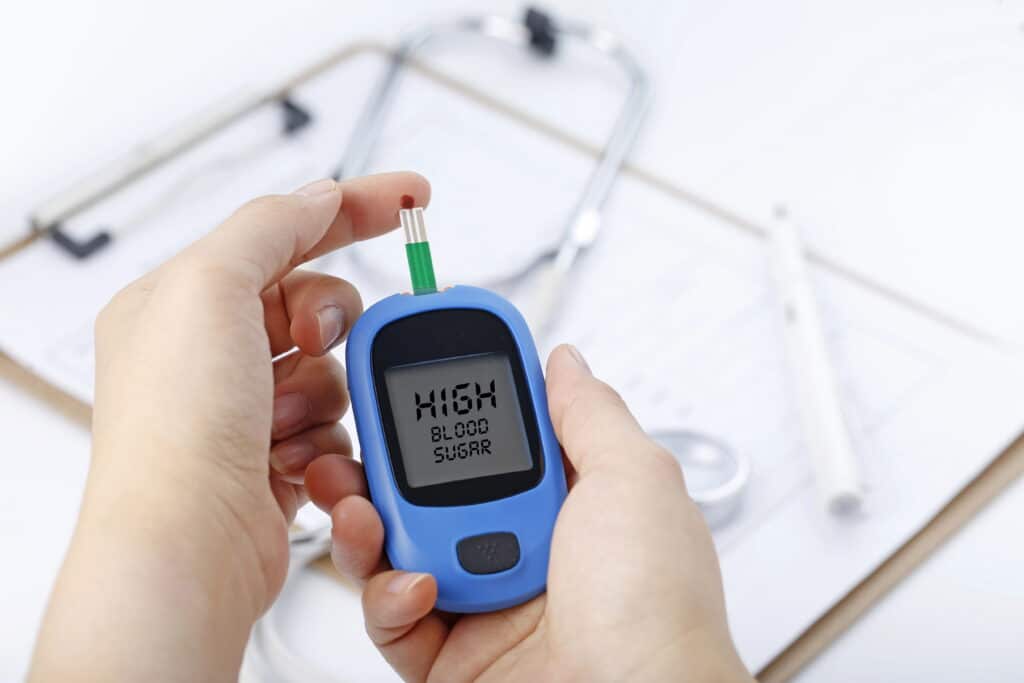
Gestational Diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and affects how the body processes glucose (sugar).

Welcome to the world of endocrinology, where we delve into the intricacies of hormone-related health issues. One such condition that affects pregnant women is Gestational Diabetes, a significant concern during pregnancy. We will shed light on what Gestational Diabetes is, its causes, risk factors, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Gestational Diabetes is a temporary form of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and affects the way the body processes glucose. While it usually occurs in the second half of pregnancy, it demands immediate attention due to potential risks to both the mother and the unborn child.
Early diagnosis and proper management are essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy and childbirth. A combination of dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, and blood glucose monitoring can help control the condition. In some cases, insulin therapy may be recommended.
At German Medical Center, we understand the significance of specialized care during pregnancy, especially when dealing with endocrinological conditions like Gestational Diabetes. Our team of experienced endocrinologists and obstetricians is dedicated to providing comprehensive and personalized care to expectant mothers.
Remember, knowledge is power, and with the right guidance and care, you can embrace motherhood with confidence even in the face of Gestational Diabetes.
Our team of experts are passionate about providing only the best quality care and treatment to their patients.

Endocrinology Treatment
Thyroid diseases refer to a group of medical conditions that affect the thyroid gland....
Early diabetes treatment is key to preventing complications and managing the condition effectively....
Pituitary and growth disorders are medical conditions that affect the function of the pituitary gland and the process of growth in the human body...

Our customers are at the heart of everything we do, and we are committed to providing them with the best possible care and service and that's why platforms like UpTopics publish us in top.


(4.5)
Based on 174 Google Reviews

Partner with:
Partner with:


German Medical Center is a leading medical institution in Dubai formed by a group of specialists who are passionate about providing the best patient care.
Fill out our easy online form to book an appointment with German Medical Center. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing you with personalized care and guidance every step of the way. Don't wait, take charge of your well-being and schedule your appointment now!